Edit Content

Wood Product Supply
Our Contact
Edit Content

Wood Product Supply
Our Contact
Edit Content

Wood Product Supply
Our Contact
Edit Content

Wood Product Supply





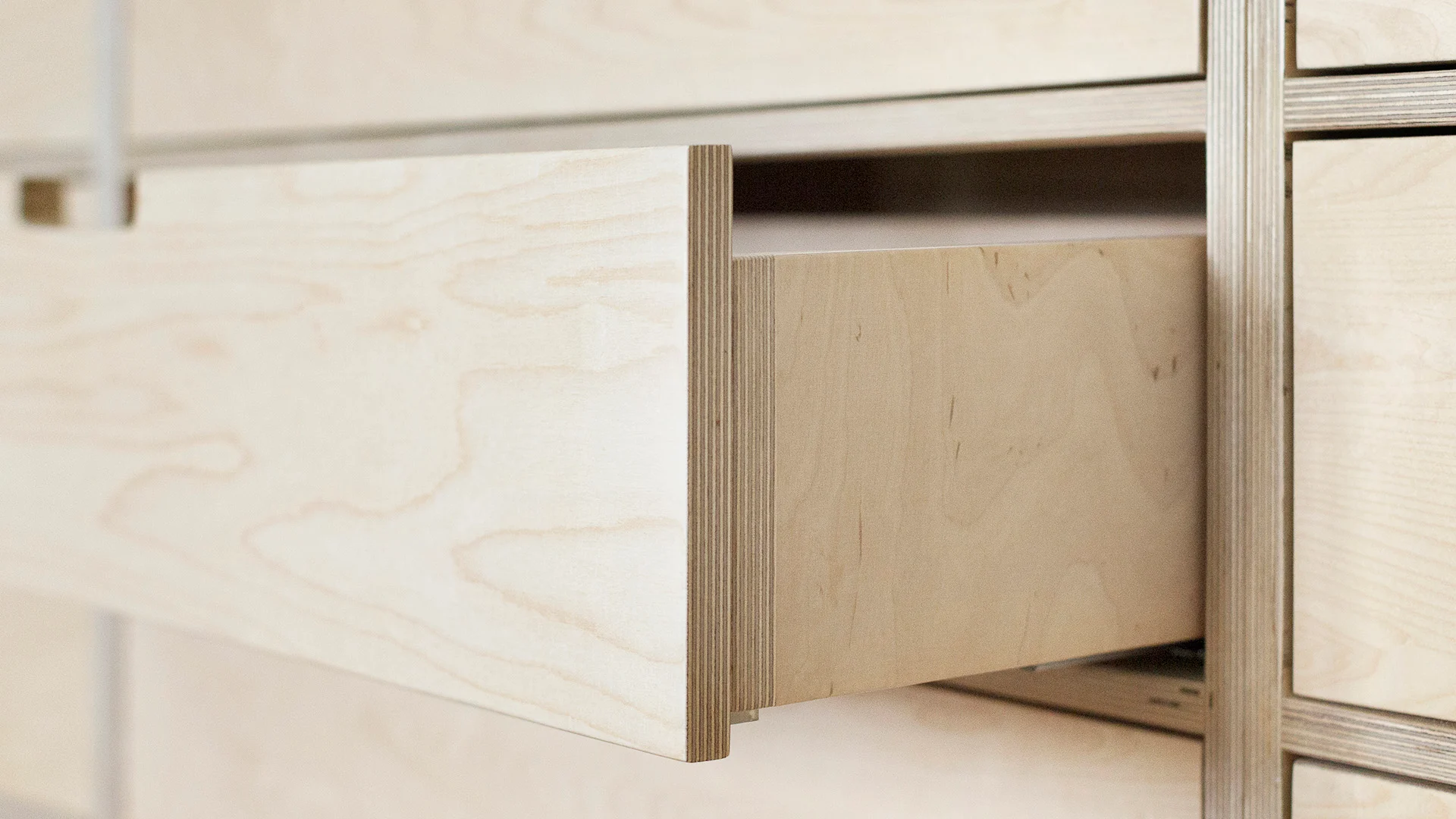
Plywood is a composite wood panel made from thin layers of wood veneer, known as plies or veneers, bonded together with adhesive under heat and pressure. The arrangement of these layers is what lends plywood its exceptional strength, stability, and resilience. Plywood is manufactured by laying long grain sheets on short grain, called cross-graining. This method of laying has several important benefits: it reduces the tendency of wood to split when nailed at the edges; it reduces expansion and shrinkage, providing improved dimensional stability; and it makes the strength of the panel consistent across all directions. There is usually an odd number of plies, so that the sheet is balanced—this reduces warping. Because plywood is bonded with grains running against one another and with an odd number of composite parts, it has high stiffness perpendicular to the grain direction of the surface ply.
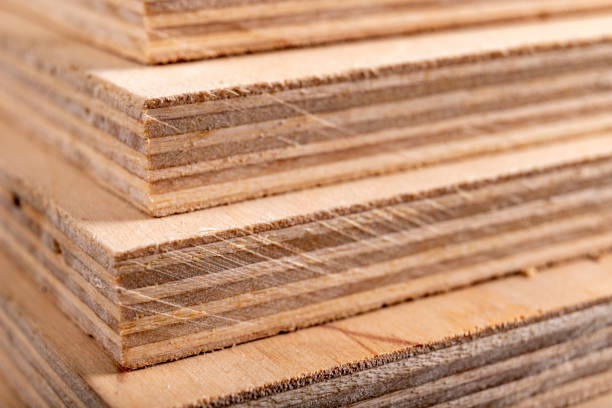
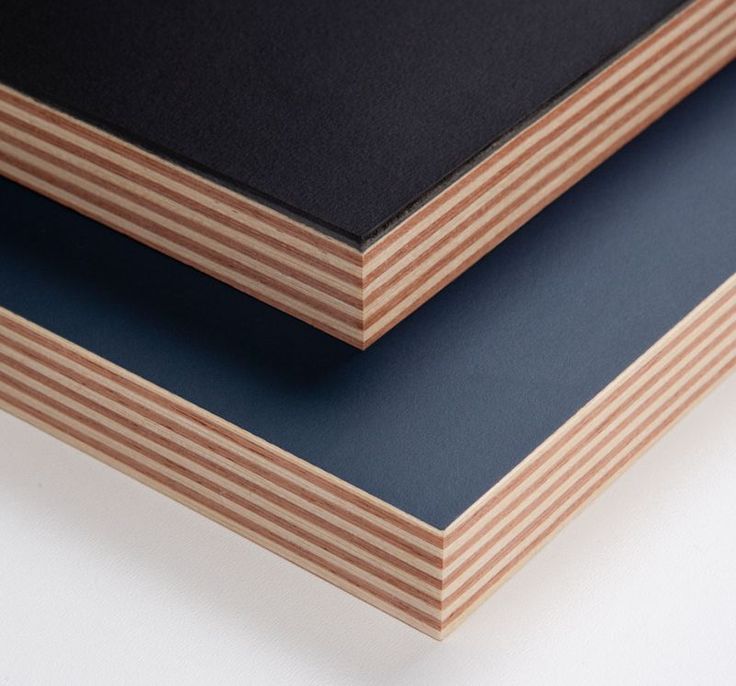
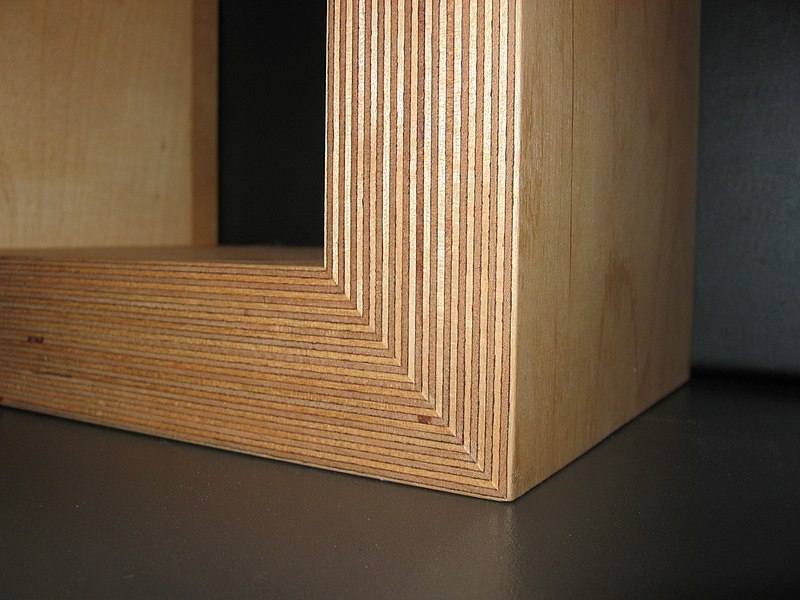
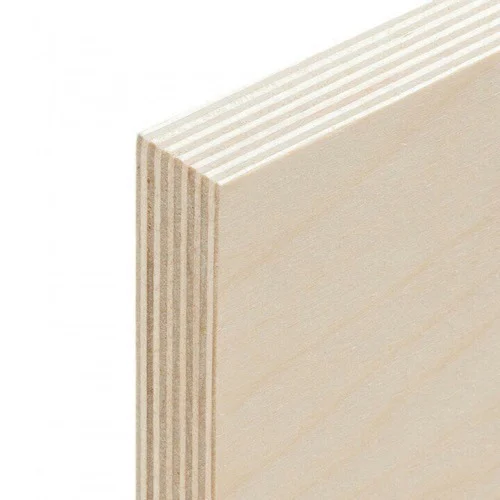






Size of plywood:
Thicknesses:
Thickness varies from 2.7mm to 30mm for interior and exterior plywood.
For film face thicknesses varies from 15mm to 24mm
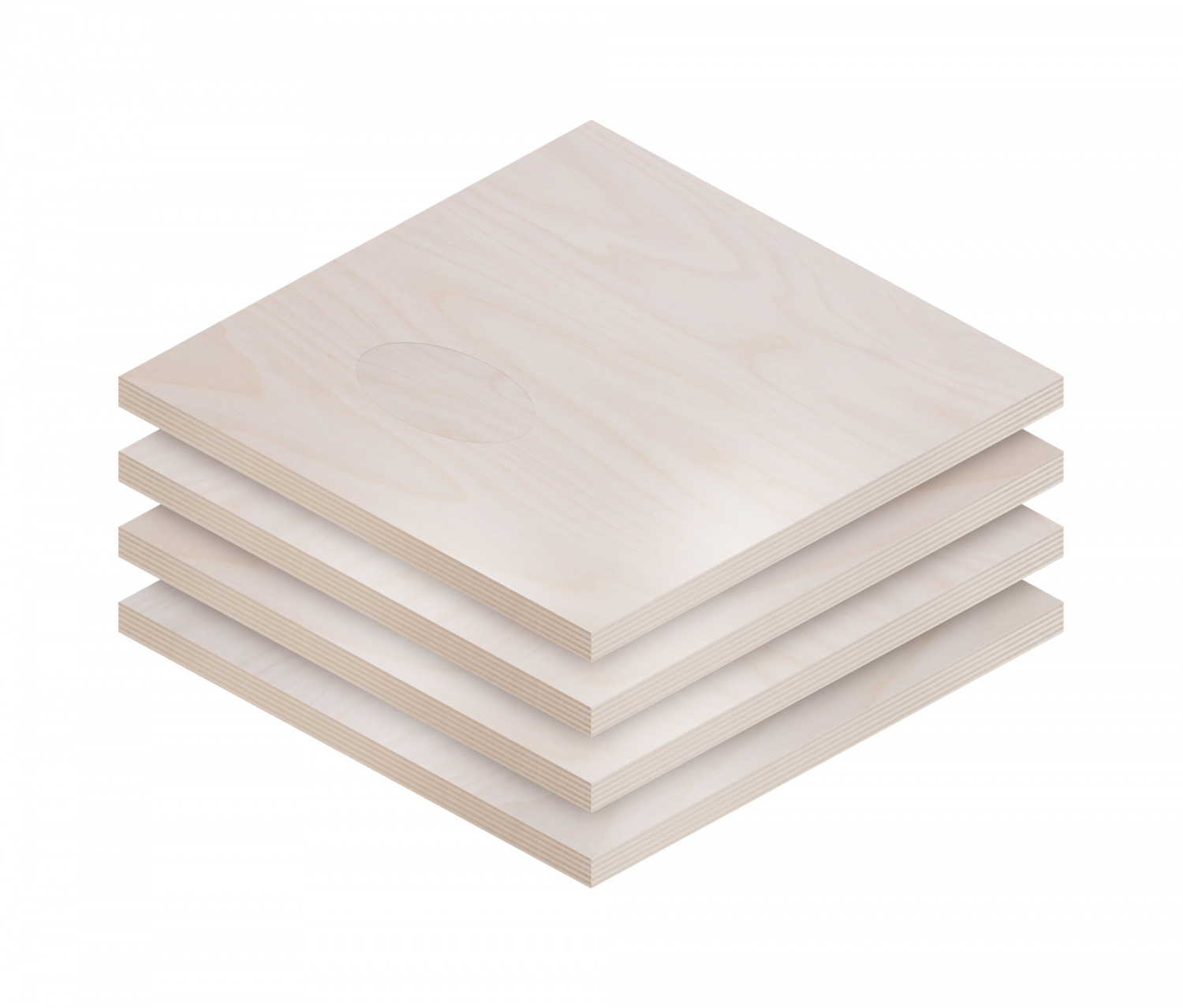
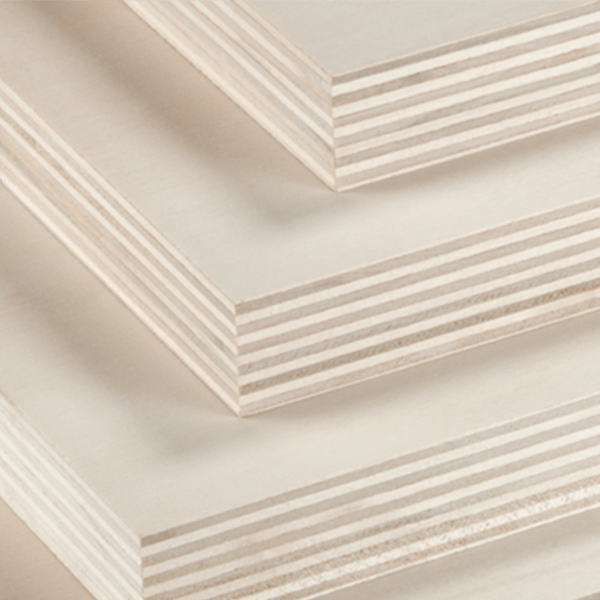
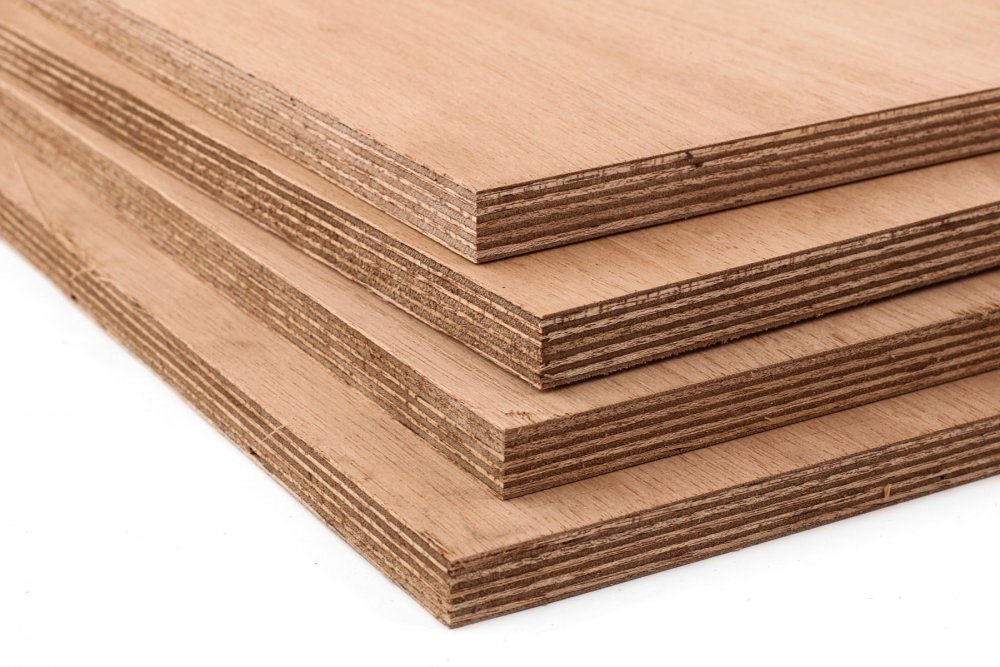
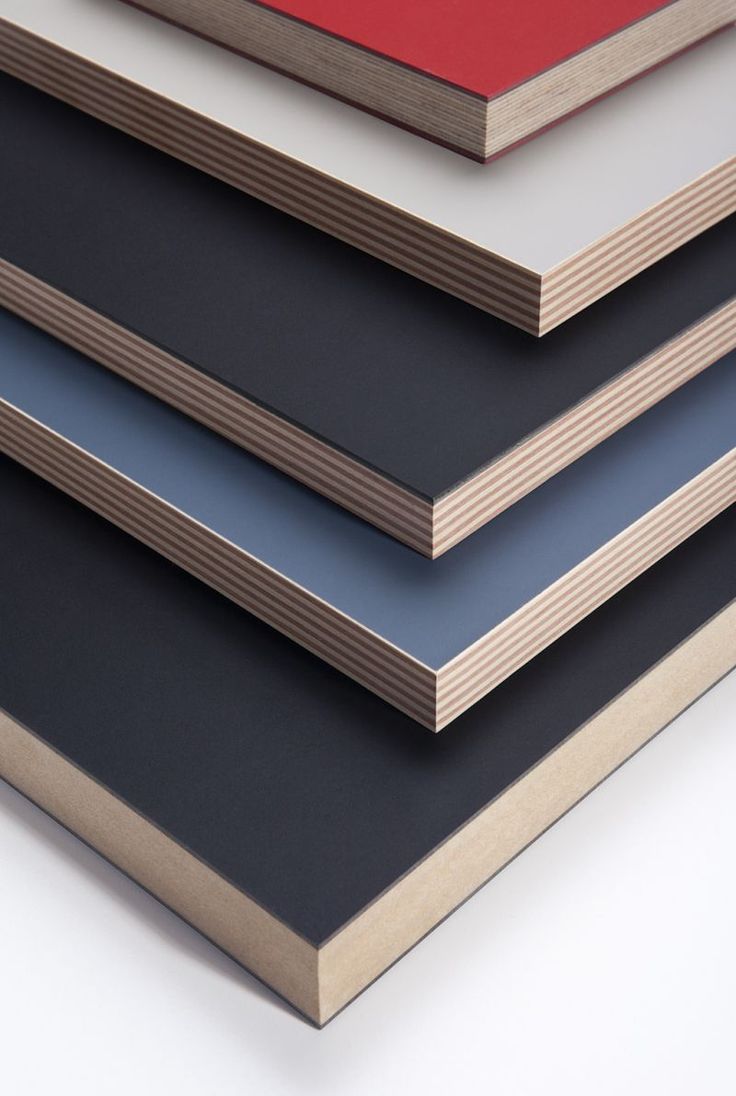






Crafting plywood is a meticulous process that involves several stages of production:

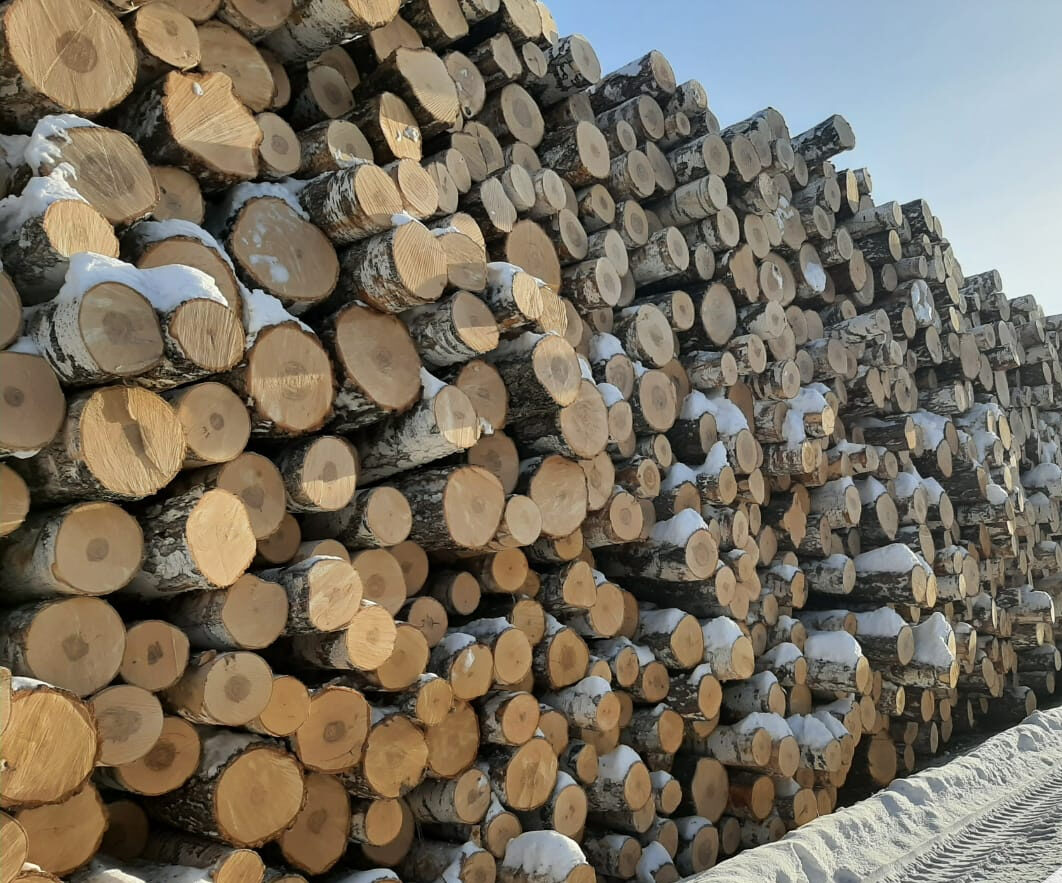
 Log Selection
Log SelectionHigh-quality logs are carefully selected based on their species, size, and wood grain characteristics.
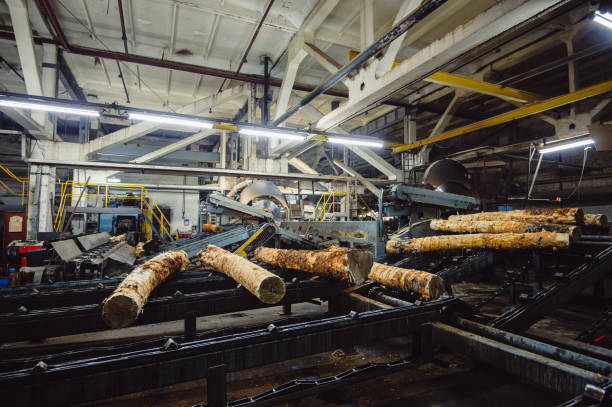



 Peeling
PeelingThe selected logs are rotary-cut or sliced into thin veneer sheets using specialized peeling machinery.

 Drying
DryingThe veneer sheets undergo a drying process to remove excess moisture and prevent warping.

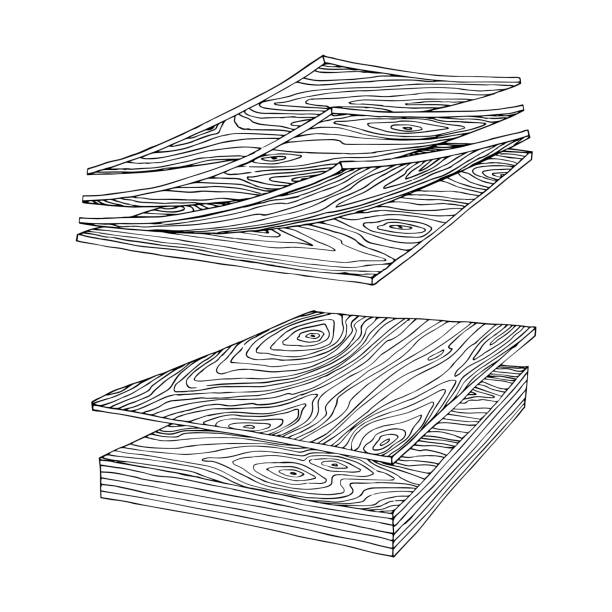
 Assembly
AssemblyThe dried veneers are arranged in a cross-grain orientation, with each layer perpendicular to the adjacent one, to maximize strength and stability.

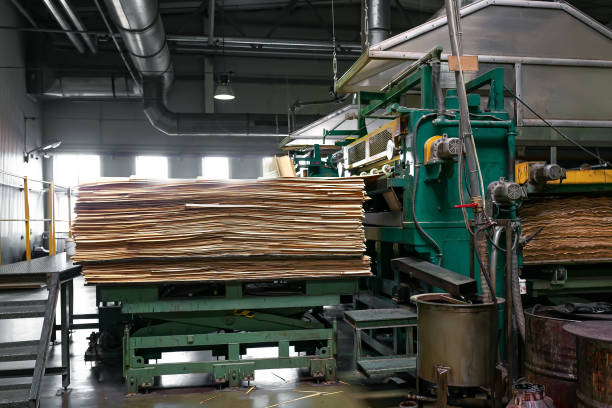
 Gluing
GluingAdhesive, typically a resin-based compound, is applied between the veneer layers to bond them together.
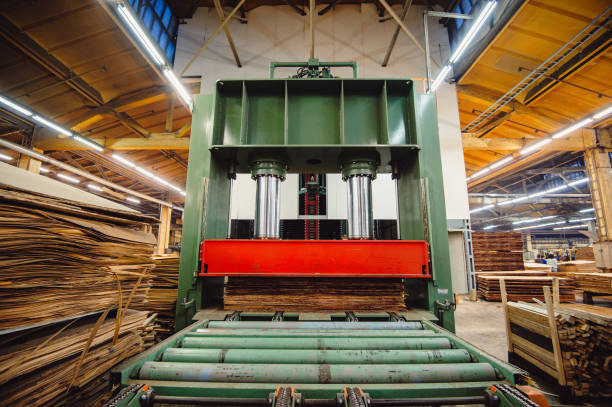



 Pressing
PressingThe assembled veneer stack is placed in a hydraulic press, which undergoes heat and pressure to facilitate bonding and curing of the adhesive.


 Trimming and Finishing
Trimming and FinishingOnce cured, the plywood panels are trimmed to size, sanded, and finished according to the desired specifications.
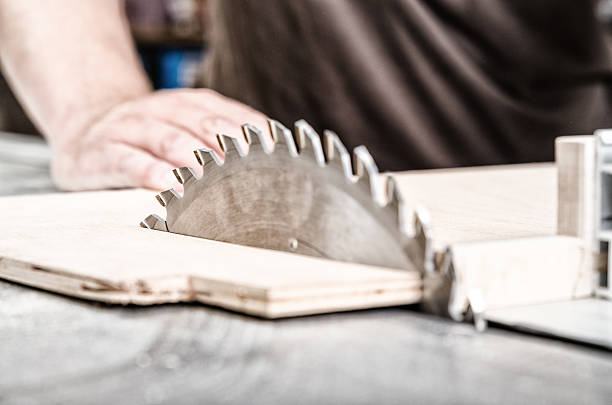





Plywood’s versatility knows no bounds, making it an indispensable material in a wide range of applications:








The concept of plywood traces its roots back to ancient Egypt and China, where early civilizations utilized thin wooden panels for various applications. However, it wasn’t until the early 20th century that modern plywood as we know it today began to take shape.
